Alternative Italian feedback circuit
Designations
M - timer motor
The electromechanical timer operating principle is based on rotation of the shaped drum sequencer by the micromotor. The drum periodically switches over the timer contacts. Thus, time is counted down only when the micromotor is powered.C - compressor
The refrigeration unit operating principle is based on physical processes in its pipelines during coolant circulation in them. Circulation is provided by refrigeration unit compressor. Its operation causes intense cooling of the refrigeration unit evaporator.F - fan
Heat exchange between the refrigeration unit evaporator surface and food products inside the refrigerator is provided by the air flow created by the No Frost system fan.R - defrost heater
The moisture in the air, blowing down the intensely cooled evaporator of the No Frost system, gradually settles on its surface as frost. The heater, attached on the evaporator, assures its heating for frost melting and surface cleaning. It is needed to prevent formation of an excessively thick frost layer, impairing effectiveness of heat exchange between the evaporator and air flow.DT - defrost thermostat
Temperature of the No Frost system evaporator must be monitored during automatic defrost, so as to switch off the heater in time. The defrost thermostat is used for temperature monitoring. Its contacts open at a temperature slightly above the frost melting temperature.Interactive Circuit Diagram
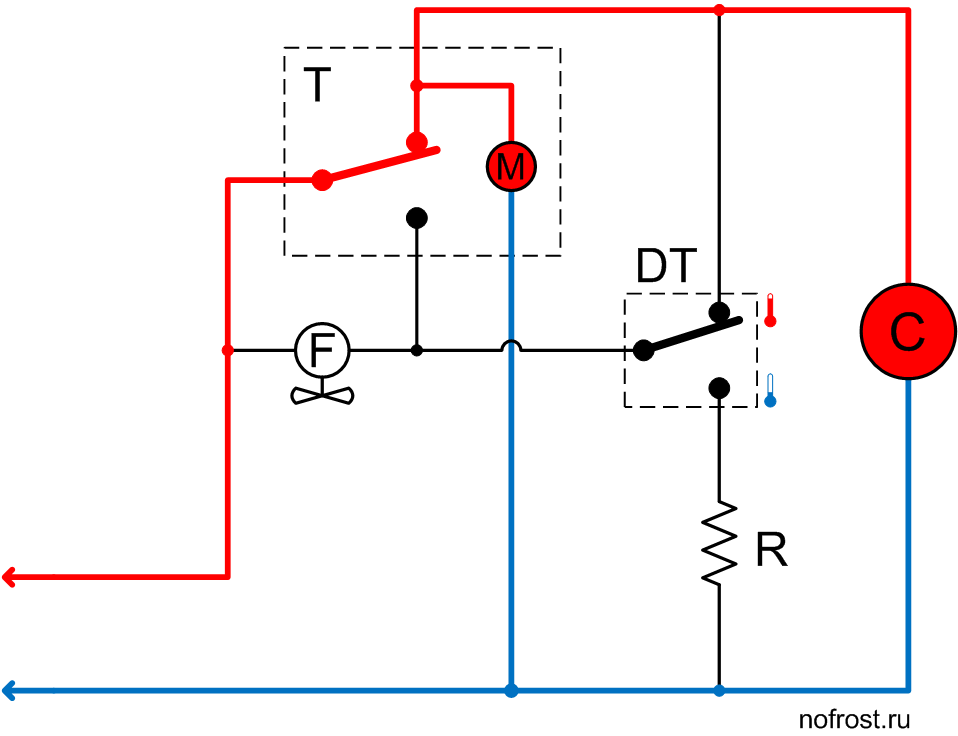
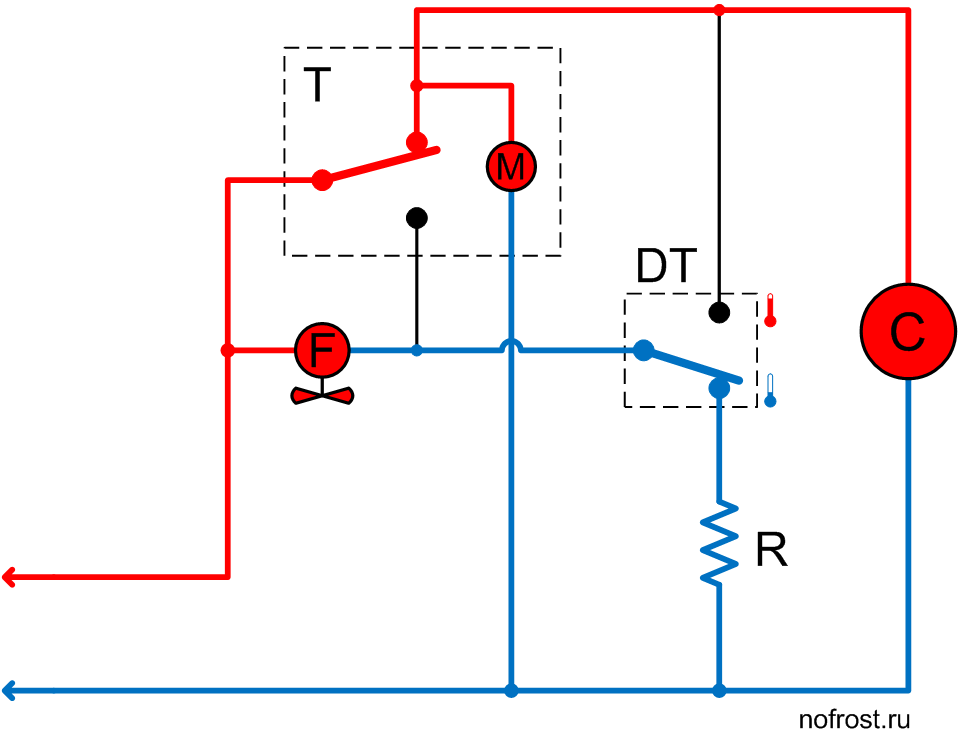
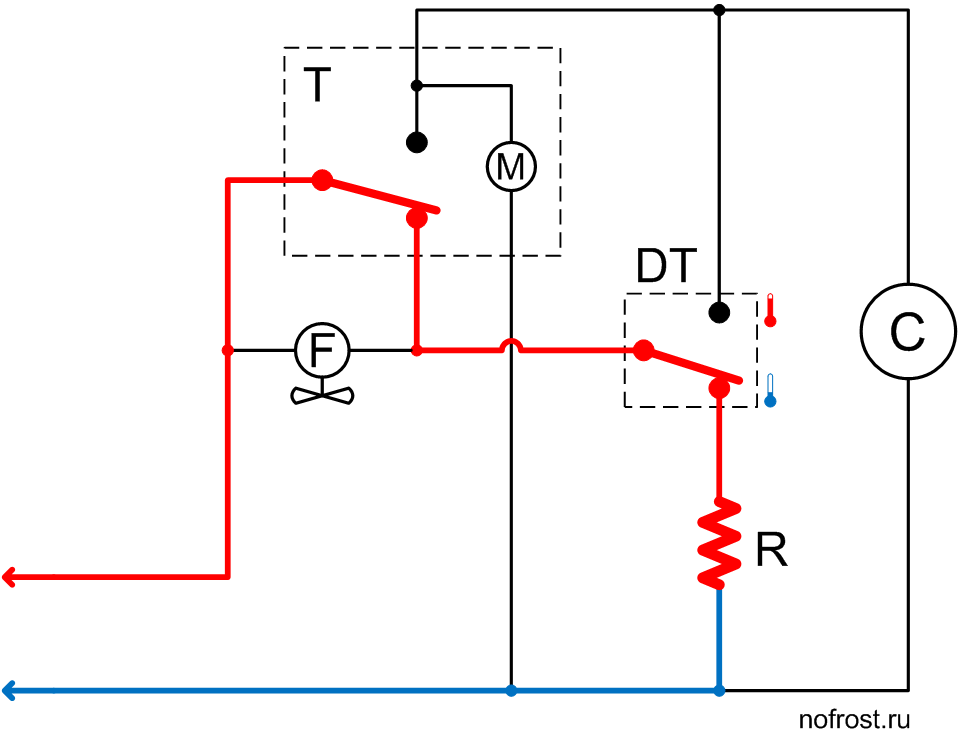
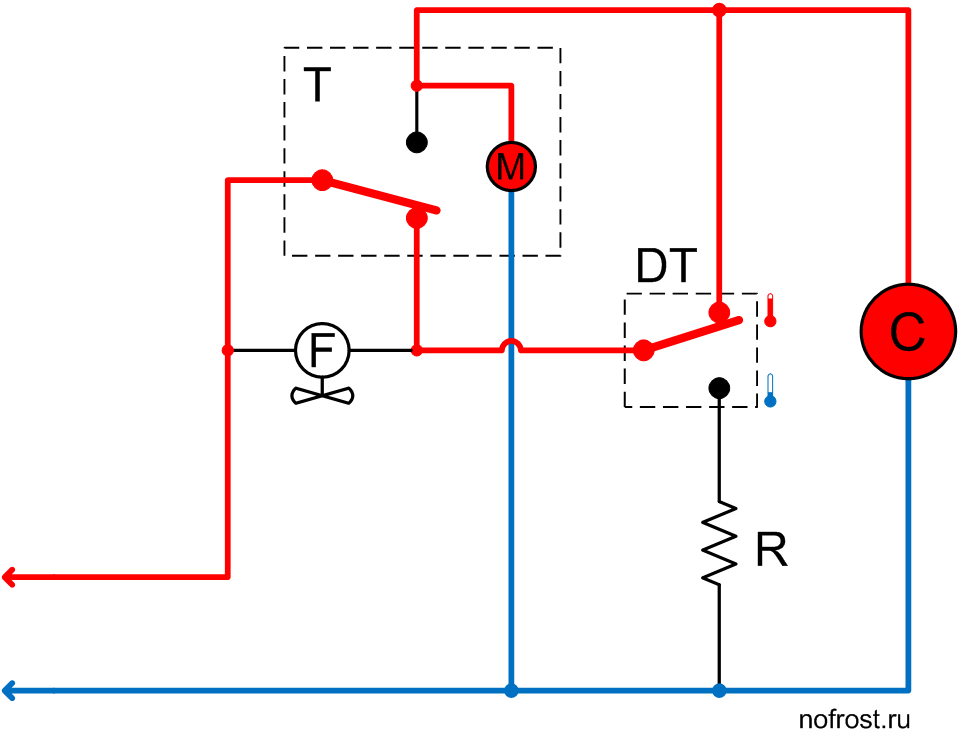
The system is in the mode of initial rapid cooling and the defrost thermostat contacts are set to the position corresponding to the warm evaporator. The compressor is powered via the timer, while the fan is de-energized.
The system operates in this mode only for several minutes. Usually this time is enough for sufficient cooling of the evaporator and switchover of the defrost thermostat contacts to the lower position according to the diagram, corresponding to the cold evaporator.
The evaporator has cooled down sufficiently and the defrost thermostat contacts have switched over to the lower position according to the diagram, supplying power to the fan via the defrost heater.
It is the main system operation mode, in which it stays for the next few hours, cooling products in the refrigerator boxes.
The system has set to the defrost mode. The timer de-energized the compressor and powered up the defrost heater. The fan and timer motor are de-energized.
Evaporator temperature is low as yet, that’s why the defrost thermostat contacts are in the lower position according to the diagram. The timer motor is de-energized. Evaporator temperature slowly rises due to heater operation.
The heater warmed up the evaporator to above the frost melting temperature and the defrost thermostat contacts have switched over, de-energizing the heater and powering up the compressor. The timer motor is also operating. However, the fan is still de-energized.
We see there is no pause. The system activates the compressor right after heater switch-off. While the system operates with the compressor ON and the fan OFF, the cooled evaporator successfully recovers the heat generated during defrost.
The system operates in this mode for several minutes, and then the timer will switch over its contacts.